Picking a new router isn’t about chasing the “best” model on the market. It’s about finding the right one for your home. The perfect fit always comes down to three things: your home's size, the number of devices you connect, and how you actually use the internet. Nailing this assessment from the get-go is the most important part of the entire process.
Finding Your Perfect Router Match
Before you get bogged down in a sea of tech specs and confusing acronyms, let’s pin down what your home network really needs. A one-size-fits-all router simply doesn't exist, and trying to find one usually leads to one of two outcomes: you either overspend on features you'll never touch, or you cheap out and end up with a router that can't keep up.
I like to compare it to buying a car. You wouldn't get a two-seater sports car for a family of five, and you wouldn't buy a minivan if you're just commuting solo across the city. The logic is identical here. Someone in a studio apartment streaming Netflix has completely different needs than a family in a three-story house juggling smart lights, security cameras, gaming consoles, and a couple of people working from home.
Define Your Environment and Usage
First things first, let's take a quick inventory of your setup. This simple reality check will steer every other decision you make down the line.
-
Home Size and Layout: Are we talking about a small apartment under 1,500 square feet? A medium, single-story home? Or a large, multi-level house with Wi-Fi killers like brick walls or a finished basement?
-
Device Count: How many gadgets will be fighting for a signal? Count absolutely everything—laptops, phones, smart TVs, speakers, thermostats, lightbulbs, and even those smart plugs. A modern smart home can easily have over 30 devices online at once.
-
Primary Internet Activities: What's your daily grind look like online? Are you mostly just browsing and checking emails, or are you pushing your connection with demanding tasks like 4K streaming, competitive online gaming, or constantly downloading massive files?
Answering these questions gives you a clear profile to work from. For example, a big, sprawling house immediately points toward a mesh Wi-Fi system. A high device count tells you that a router with modern tech like MU-MIMO isn't just a nice-to-have, it's a necessity.
To give you a head start, this quick table maps common scenarios to the right type of router.
Quick Router Recommendation Guide
Use this table to quickly align your home setup with the right type of router, giving you a clear direction from the start.
| Primary Use Case | Recommended Router Type | Must-Have Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Small apartment, 1-2 users, basic streaming | Basic Dual-Band Router | Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) |
| Medium home, family use, 4K streaming & gaming | Mid-Range Wi-Fi 6 Router | MU-MIMO, QoS |
| Large or multi-story home with dead zones | Mesh Wi-Fi System | Multiple satellite nodes |
| Smart home with 30+ devices, heavy usage | High-End Wi-Fi 6/6E Router | Tri-Band, OFDMA |
This should help you zero in on the category of router that makes the most sense before you start comparing specific models.
This decision tree gives you a great visual for how to narrow things down based on these core factors.
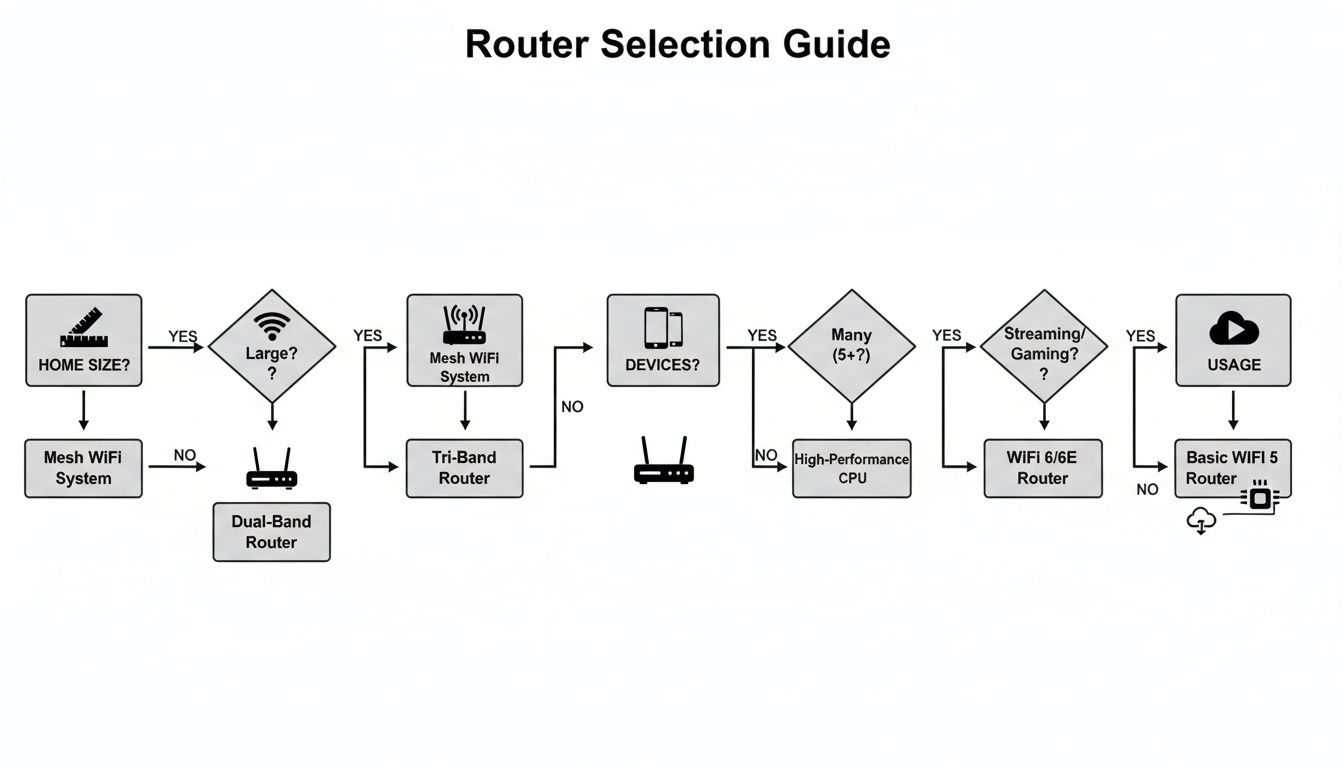
As you can see, your home's physical layout is the first filter. After that, it’s all about the sheer volume of connections and what you're doing with them every day.
By answering these three simple questions first, you build a foundation that prevents buyer's remorse and ensures your new router is a valuable, long-term investment rather than a source of daily frustration. It's the most effective way to learn how to choose routers wisely.
Breaking Down the Tech Specs: Wi-Fi Standards and Speeds

If you've ever shopped for a router, you know the feeling. You're hit with a barrage of alphabet soup and numbers: Wi-Fi 6, AX3000, Dual-Band. It can feel overwhelming, but getting a handle on these terms is the first real step to picking a router that won't let you down.
Think of Wi-Fi standards like generations of a car. Each new model gets faster, more efficient, and better at handling traffic. Thankfully, the industry has simplified the naming, moving from confusing codes like "802.11ac" to the much friendlier numbered system we have today.
What's in a Number? A Guide to Wi-Fi Generations
The Wi-Fi standard is probably the single most important detail on the box. It determines the router's maximum speed, how efficiently it talks to your devices, and how well it copes when your whole family is online at once. Here’s the rundown on what you’ll actually see in stores.
-
Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac): For a long time, this was the workhorse of home networking. You'll still find it on budget routers, and honestly, it's fine for smaller homes with just a few devices. It can handle HD streaming and web browsing without a problem, but it starts to buckle under the pressure of a modern smart home.
-
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax): This is the new baseline. The biggest win for Wi-Fi 6 isn't just a speed boost—it's about smarts. It was built from the ground up to juggle dozens of devices at the same time without slowing to a crawl. If you’ve got smart lights, speakers, cameras, and multiple people streaming, this is where you should start.
-
Wi-Fi 6E: This standard is essentially Wi-Fi 6 with a VIP lane. It adds access to the brand-new 6 GHz frequency band—a clean, uncongested superhighway for your newest gadgets. If you live in a crowded apartment building where everyone's Wi-Fi is fighting for airtime, or you have cutting-edge devices, Wi-Fi 6E is a true game-changer.
The global router market is booming, expected to hit $75 billion by 2032, largely because our homes are getting smarter. With over 15 billion IoT devices already connected worldwide, a Wi-Fi 6 or 6E router is the only way to make sure your network is ready for the future. You can explore more data on the growing router market and see the trends for yourself.
My Takeaway: For the vast majority of smart homes, a Wi-Fi 6 router is the sweet spot. It delivers the performance you need for a busy, connected household without the premium price tag of the absolute latest tech.
What Do Router Speed Numbers Like AX3000 Really Mean?
Right next to the Wi-Fi standard, you'll see a code like AC1900 or AX3000. This number isn't the speed you'll get from your internet plan. It’s the router's total theoretical speed across all its wireless bands combined.
The letters are a simple giveaway: 'AC' means Wi-Fi 5, and 'AX' means Wi-Fi 6. The number is the sum of the maximum speeds. For instance, an AX3000 router might have a 2.4 GHz band rated for 574 Mbps and a 5 GHz band rated for 2402 Mbps. Add them up, and you get roughly 3000.
No single phone or laptop will ever get that full 3000 Mbps. Instead, think of it as the router's total bandwidth pie. A bigger number means there's more pie to slice up and share among all your devices, which helps everything run smoother.
Dual-Band vs. Tri-Band: How Many Lanes Do You Need?
So, what are these "bands"? A router broadcasts its signal on different radio frequencies, kind of like a radio station.
-
Dual-Band: This is the most common setup, offering two bands. The 2.4 GHz band is the long-range specialist—it goes through walls better but is slower and more prone to interference from microwaves and old cordless phones. The 5 GHz band is the speedster—it's much faster and less crowded but has a shorter reach. Good routers automatically "steer" your devices to the best band for the job.
-
Tri-Band: These routers add a second, independent 5 GHz band (or the 6 GHz band on Wi-Fi 6E models). This is like adding another lane to your Wi-Fi highway to prevent traffic jams. You can dedicate one band to demanding tasks like 4K streaming or online gaming, leaving the others free for your smart plugs and thermostats. For mesh systems, this extra band is often used as a private, high-speed connection between the router and its satellites, which drastically improves performance.
For a family with a gamer, a couple of 4K streamers, and a house full of smart gadgets, a tri-band router can bring a very real improvement in network stability. If you're in a smaller household, a quality dual-band router will serve you perfectly well.
Single Router vs. Mesh System: Which Is Right for Your Space?
Once you've got a handle on the tech specs, you'll face your next big decision: should you go with one powerful, traditional router or a multi-point mesh Wi-Fi system? This isn't about which one is "better" in a vacuum. It’s all about matching the hardware to the unique size and shape of your home.
Getting this choice right is the single biggest factor in banishing those frustrating Wi-Fi dead zones for good.
For a lot of homes, a single, high-quality router is all you'll ever need. It’s the classic setup—a central hub that broadcasts your Wi-Fi signal from one spot. If you live in an apartment or a single-story home under 1,500 square feet, this is often the simplest and most cost-effective way to get great coverage.
The problems start when you introduce challenges like multiple floors, a sprawling layout, or thick walls made of brick or plaster. A single router's signal gets weaker the farther you are from it, creating those dead spots where your connection completely vanishes.
The Case for a Powerful Single Router
Don't write off the standalone router just yet. In the right environment, it delivers unbeatable performance for your money. A high-end single router can push out incredibly fast speeds with low latency, which is perfect for a gamer in a one-bedroom apartment or a couple in a smaller home who need flawless 4K streaming and video calls.
Think of it like a powerful speaker. In one room, it can fill the space with amazing sound. But if you try to listen from three rooms away, the quality drops off a cliff. A single router operates on the same principle.
A single router excels in concentrated spaces. It's the ideal choice for apartments and smaller homes where you can place it in a central location to cover the entire area effectively without needing extra hardware.
A single router is probably your best bet if you fall into these categories:
- Smaller Living Spaces: Perfect for apartments and homes under 1,500 square feet.
- Open-Concept Layouts: It works best when there are fewer walls and obstacles for the signal to fight through.
- Budget-Conscious Buyers: A top-of-the-line single router often costs less than even an entry-level mesh system.
- Performance-Focused Users: Gamers and power users who are physically close to their router can take advantage of its direct, high-speed connection.
When to Choose a Mesh Wi-Fi System
If you’ve ever walked to the far side of your house and watched your Wi-Fi bars drain away, a mesh system was practically designed for you. Instead of blasting a signal from one point, a mesh network uses multiple devices (called "nodes") that work together to blanket your home in a seamless web of Wi-Fi.
One node connects to your modem and acts as the main router. You then place one or more satellite nodes around your home. They all talk to each other, intelligently passing your phone, laptop, or smart device to the node with the strongest signal as you move around. This is what finally kills dead zones and gives you a consistent, reliable connection everywhere—the basement, the attic, and even out on the patio.
For anyone who's struggled with bad coverage, it's a much more elegant and effective fix than the older methods detailed in guides on how to extend Wi-Fi range.
This kind of setup is a lifesaver in homes with layouts that are notoriously hostile to Wi-Fi signals.
- Large or Multi-Story Homes: A mesh system is the definitive solution for any space over 2,000 square feet or houses with two or more floors.
- Homes with Tricky Layouts: If your home is long and narrow (like a ranch-style) or has a lot of corners and hallways, mesh nodes can push a strong signal into every nook and cranny.
- Properties with Signal Blockers: Brick, concrete, or stone walls are Wi-Fi killers. Placing a mesh node on either side of an obstacle like that solves the problem instantly.
The main tradeoff here is cost. Mesh systems are usually more expensive than single routers. But for anyone living in a larger or more complex home, it's an investment that pays for itself with reliable, frustration-free internet in every single room.
Must-Have Features for a Connected Smart Home

Once you've sorted out the basics like speed and coverage, it's time to look at what really makes a smart home router shine: how it manages traffic. Think of your router as an air traffic controller. With dozens of devices—from security cameras and smart speakers to thermostats and light bulbs—all clamoring for bandwidth, things can get chaotic fast.
Without the right features, you end up with buffering video calls, laggy online games, and smart devices that just won't respond. Let's dig into the key technologies that prevent this digital gridlock and keep your network running smoothly.
Ending Network Congestion With MU-MIMO and OFDMA
Imagine your router is a pizza delivery driver. An old-school router could only take one pizza to one house at a time, forcing everyone else to wait their turn. That’s fine with a few devices, but in a busy smart home, it creates a massive traffic jam.
That's where MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output) comes in. This technology allows your router to talk to multiple devices at the same time. Instead of one delivery at a time, a router with MU-MIMO can serve several devices at once, which dramatically cuts down on wait times and makes the whole network feel faster for everyone.
OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access), a signature feature of Wi-Fi 6, takes this a step further. If MU-MIMO lets the driver deliver to multiple houses on one trip, OFDMA lets them pack the car with smaller orders for different destinations, all delivered in the same run. It splits a single Wi-Fi channel into smaller pieces to serve many devices with small data packets simultaneously—perfect for the constant, tiny updates from your smart home gadgets.
These two technologies work in tandem to create an incredibly efficient network, ensuring your smart thermostat’s check-in doesn’t torpedo your 4K movie night.
Prioritizing Your Traffic With Quality of Service
Let’s be honest: not all internet traffic is equally important. A work video conference is far more sensitive to lag than a background app update. This is where Quality of Service (QoS) becomes an absolute game-changer.
QoS is a setting that lets you tell your router what traffic to prioritize. You can put specific applications (like Zoom or your favorite online game) or specific devices (like your work laptop) in the express lane. When the network gets congested, the router makes sure your priority traffic gets the bandwidth it needs first.
Here's a real-world scenario:
- You’re on a crucial work video call from your home office.
- At the same time, your kids start streaming an HD movie in the living room.
- Without QoS, both streams compete for bandwidth, and your call could start to stutter and pixelate.
- With QoS enabled and your work laptop prioritized, the router gives your video call first dibs on bandwidth, keeping it perfectly smooth.
This kind of control is a must-have for anyone working from home or for families with lots of different internet needs.
By intelligently managing data flow, QoS transforms your network from a digital free-for-all into a highly organized system. It’s the feature that guarantees your most important connections stay stable, no matter what else is happening online.
Boosting Signal Strength With Beamforming
Older routers broadcast their Wi-Fi signal in all directions, like a bare lightbulb lighting up an entire room. This is pretty inefficient, wasting a lot of signal in places where you don't even have devices. Beamforming offers a much smarter way to do things.
Instead of broadcasting everywhere, a router with beamforming finds where your connected devices are and focuses the Wi-Fi signal directly at them. It’s like swapping that bare bulb for a powerful spotlight aimed right at your phone, laptop, or smart TV.
This focused signal means you get a stronger, faster, and more reliable connection, especially the farther you are from the router. It helps cut through interference and keeps your performance solid even as you move around the house.
It's clear that consumers are voting with their wallets for these smarter features. In the third quarter of 2025, the market for traditional access routers dropped by a staggering 25% year-over-year. Meanwhile, router solutions with integrated security and management features jumped by 21%. People are moving away from "dumb" routers and toward intelligent ones that can handle the demands of a modern home.
For anyone building out a smart home, getting a handle on the broader IoT security challenges is critical. These router features are a great first line of defense, but it's also worth understanding the languages your devices use to speak to each other. You can learn more by checking out our guide on the most common smart home protocols.
Final Checks for Security and Compatibility

Alright, you've done the heavy lifting. You've sized up your home, wrestled with the tech specs, and weighed the pros and cons of a single router versus a full-blown mesh system. Before you hit that "buy" button, let's run through a couple of final checks. This is the step that separates a smooth setup from a weekend of frustration.
First up, security. The absolute must-have feature on any new router today is WPA3. This is the latest security standard, and it's a huge leap forward from the older WPA2 protocol. It provides much stronger encryption, making your network a tougher nut to crack for intruders. In a smart home filled with personal data and connected devices, settling for anything less than WPA3 is a risk you just don't need to take.
Confirm ISP Compatibility
Next, you have to make sure your shiny new router will actually work with your Internet Service Provider (ISP). This might sound obvious, but it's a common stumbling block. While most routers are universally compatible, some ISPs, particularly fiber providers, can have specific hardware requirements.
The easiest way to check is to hop on your ISP's website or give their support line a quick call. Just ask if they have a list of compatible third-party routers.
While you're talking to them, it's also a great time to ask if you can use your own modem. The combo modem/router unit you're likely renting for a monthly fee can often be replaced. Buying your own modem and pairing it with a powerful new router not only saves you cash over time but also gives you far more control over your network’s performance and settings.
Essential Management Features
A good router isn't just about speed; it's also about control. Two features that I consider non-negotiable for any modern home are guest networks and parental controls. These aren't just fancy extras anymore—they're essential tools for managing a busy, secure smart home.
-
Guest Networks: This feature creates a completely separate Wi-Fi network for your visitors. It gives them internet access without giving them a backdoor to your main network where your computers, cameras, and personal files live. It’s a simple, elegant way to boost your security.
-
Parental Controls: Router-level parental controls have gotten incredibly sophisticated. You can now do things like block specific types of content, set time limits for certain devices (think shutting off the kids' tablets at 9 PM), or even pause the internet entirely with a single tap on an app.
Getting these settings right from the start is crucial. For more tips on locking things down, check out these home network security best practices.
A crucial final check after choosing your router is learning how to effectively start securing your WiFi network to protect all connected devices. This initial setup is your first line of defense.
This demand for better security and network management isn't just a local thing. Globally, the fastest-growing router market is Asia Pacific, which is expected to make up 29.40% of the entire market by 2025. This growth is largely driven by dense urban areas where robust security is needed to manage a sea of overlapping networks—a situation becoming more common everywhere.
A Few Final Questions Before You Decide
Even with a shortlist in hand, you probably have a few nagging questions. That's completely normal. Choosing the right router feels like a big decision, and it’s smart to iron out the last few details. Let’s walk through some of the most common questions I hear, so you can buy your next router with total confidence.
Think of this as the last sanity check before you pull the trigger.
How Often Should I Replace My Router?
Honestly, you should plan on upgrading your router every 3-5 years. This isn't just about chasing the latest shiny object; it’s about keeping your network fast and secure. Wi-Fi standards move forward, and an old router can easily become the slowest link in your chain, strangling the internet speeds you pay for.
Even more important is security. After a few years, manufacturers often stop pushing security patches to older models. That can leave your entire home network wide open to new threats. If you're seeing more frequent disconnects, sluggish speeds on a fast internet plan, or your new gadgets are struggling to connect, those are all dead giveaways that it's time for an upgrade.
Key Takeaway: An aging router isn't just slow—it's a potential security risk. Upgrading every few years keeps you up to speed with modern devices and protected by the latest security protocols.
Is a More Expensive Router Always Better?
Not a chance. The "best" router isn't the one with the biggest price tag; it's the one that’s the right fit for your home. Dropping a ton of cash on a high-end gaming router for a small apartment where you just browse and stream Netflix is a complete waste of money. You'd be paying for horsepower you will literally never use.
On the flip side, trying to save a few bucks with a cheap, basic router for a large house packed with smart devices is just asking for a headache. The price tag usually reflects newer Wi-Fi standards, better processors, and extra features like a third band or sophisticated QoS controls.
The trick is to match the router's specs to what you actually do.
- Small Home, Light Use: A solid Wi-Fi 6 router is an incredible value and will serve you well.
- Large Home, Many Devices: Spending more on a mesh system is a smart investment that pays off in frustration-free coverage.
- Heavy Use (Gaming/WFH): A mid-range router with great QoS is often a better choice than a more expensive one without it.
Don't let a high price convince you it's automatically the right choice. Focus on the features that actually solve your problems.
Do I Really Need a Tri-Band Router?
For most people, a good dual-band router is more than enough. A tri-band router, which adds a second 5 GHz band, really only shines in specific situations where your network is seriously congested.
Think of it like this: a dual-band router gives you two lanes of traffic for all your data. A tri-band model adds a third, private express lane.
You should only really consider tri-band if your home fits one of these descriptions:
- Massive Device Count: You have 50+ devices all trying to talk to the network at the same time. That extra band works wonders for clearing up the digital traffic jam.
- Wireless Mesh Systems: This is where tri-band is a game-changer. The system can dedicate one entire band just for the nodes to talk to each other at high speed. This "backhaul" frees up the other two bands entirely for your devices, drastically improving the mesh network's speed and reliability.
- High-Demand Households: You’ve got 4K streaming, competitive online gaming, and dozens of smart home gadgets all running at once. The extra bandwidth can make a noticeable difference.
If that doesn't sound like your house, a powerful dual-band router will do the job just fine and save you some money.
What Is the Difference Between a Modem and a Router?
This is a classic point of confusion, mostly because internet providers love to bundle them into one box. But a modem and a router do two completely different jobs, and knowing the difference is the first step to building a better network.
The modem is your on-ramp to the internet. It plugs into the cable or fiber line from your ISP and translates that signal into something your network can understand. It's the bridge between your home and the outside world.
The router takes that single internet connection from the modem and creates your private Wi-Fi network. It lets all your devices—laptops, phones, TVs, cameras—get online at the same time. It’s the air traffic controller for your home, directing data where it needs to go.
While the all-in-one "gateway" units from ISPs are convenient, you'll almost always get better performance, more features, and more control by using a separate modem and your own high-quality router. Plus, you can stop paying those monthly equipment rental fees.
Ready to build a smarter, more connected home? The Automated Home Guide provides the expert insights and practical guides you need to make informed decisions about your technology. Explore our resources today at https://automatedhomeguide.com.












Leave a Reply