Imagine setting up a network of security cameras around your home, but instead of juggling power cords and data cables for each one, you just run a single, simple wire. That’s the magic behind Power over Ethernet (PoE), a technology that sends both power and a data connection through one standard network cable. It’s the secret to what makes a PoE security camera system so reliable and straightforward to install.
What Is a PoE Security Camera System?

Simply put, a PoE security camera system uses a network of IP (Internet Protocol) cameras that get their power and send their video footage back to the recorder all through a single Ethernet cable. This one-cable approach gets rid of the biggest headache of camera installation: running separate power lines to every corner of your property.
It’s a bit like the USB-C cable for your laptop. You can use that one port to charge the battery, transfer huge files, and even connect to a 4K monitor. PoE brings that same all-in-one convenience to your security setup. This gives you a stable, hardwired connection that isn't at the mercy of spotty Wi-Fi signals or interference from your neighbor's router.
To quickly grasp the core concepts, here's a simple breakdown of what these systems offer.
PoE Security System At a Glance
| Feature | What It Means for You |
|---|---|
| Single-Cable Solution | No need to find or install a power outlet near each camera. Less drilling, less wiring, less mess. |
| Stable, Wired Connection | Your video feed won't drop out due to weak Wi-Fi. You get consistent, reliable recording. |
| High-Quality Video | Handles large amounts of data easily, perfect for crisp 4K and high-resolution video. |
| Flexible Placement | Install cameras wherever the Ethernet cable can reach, not just where a power outlet is. |
This combination of simplicity and performance is exactly why more and more people are choosing PoE.
The Growing Demand for Reliable Security
This no-fuss, dependable approach is really catching on. The global market for PoE Security Cameras is expected to grow at a healthy 10.20% each year from 2023 to 2030, driven by homeowners and businesses wanting security they can count on. North America is leading the charge, making up about 40% of the global revenue in 2023.
When you look at wired security systems, the data is even clearer: PoE’s simple power delivery is responsible for over 69% of the revenue. You can dig into more of this data by looking at recent industry reports. This trend shows a real shift towards high-performance surveillance that just works.
Key Takeaway: The biggest win with a PoE security camera system is getting both power and rock-solid, high-definition video from a single Ethernet cable. This means a more reliable connection and a much cleaner installation.
Core Benefits of Choosing PoE
That one-cable design is a game-changer, but it’s just the beginning. People who opt for PoE systems do so for a few very practical reasons that put them head and shoulders above other options.
- Superior Video Quality: A hardwired connection gives you a dedicated, high-speed lane for your video data. This is what lets you record in crystal-clear 4K without the lag or fuzzy compression you often get with Wi-Fi cameras.
- Unmatched Reliability: Forget about Wi-Fi dead zones, network traffic jams, or interference from your microwave. A wired PoE camera is always connected and always recording. It’s the definition of set-it-and-forget-it.
- Simplified Installation: Because you only have to run one cable to each camera, the whole process is faster and cheaper. There’s no need to hire an electrician to put outlets up in your eaves or on a fence post.
- Flexible Camera Placement: Since you aren't tied to the nearest power outlet, you can finally put your cameras where they’ll do the most good—high up on a wall, on a detached garage, or overlooking a long driveway.
Understanding the Core Components of Your System
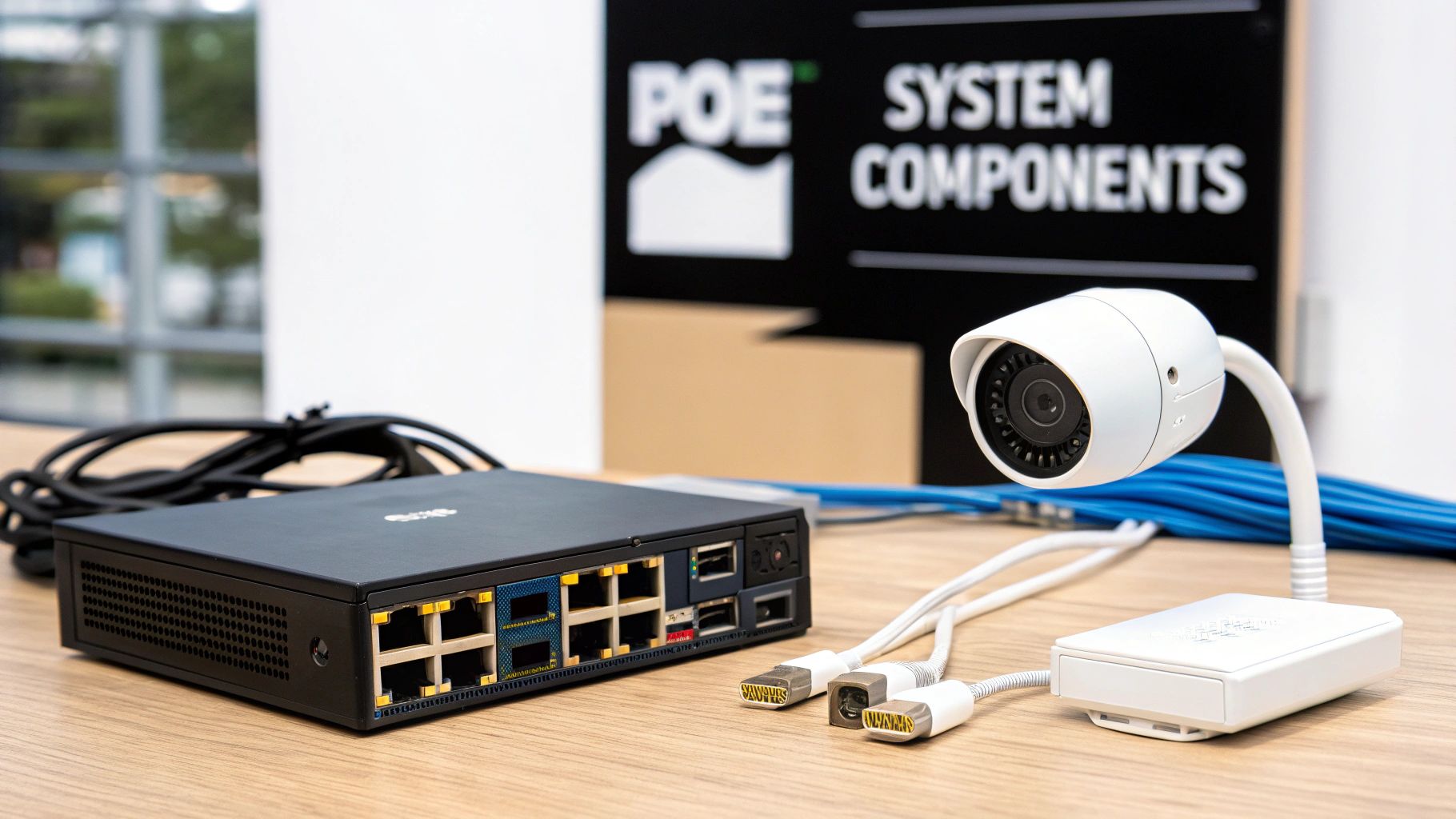

Putting together a PoE security system is a bit like assembling a team of specialists. Each piece has a critical job, and they all have to work in perfect sync to provide reliable surveillance. When you understand how these key players function, building a powerful and stable system becomes much clearer.
This isn't just about plugging in a few cameras; it's about creating a dedicated hardware ecosystem. Let’s pull back the curtain and look at the essential components you'll be working with.
The Network Video Recorder (NVR)
Think of the Network Video Recorder (NVR) as the brain of your entire operation. It's the central command hub where all the video streams from your cameras come together. The NVR is a specialized computer designed for one thing: managing and storing massive amounts of high-definition video footage, 24/7.
This is the box where you’ll connect a monitor to review recordings, tweak camera settings, and set up motion alerts. Nearly all modern NVRs also let you tap in remotely from a phone or computer, so you can check on things from anywhere in the world.
When you're picking an NVR, the first thing to look at is storage. How much video can it hold? This depends on the hard drive size, how many cameras you have, and your recording quality. For instance, a robust system might come with 3TB of local storage and support up to 16 cameras, giving you plenty of room to record continuously without constantly overwriting old footage. You can get a good feel for the components in popular PoE security camera system kits on Security.org.
High-Definition PoE Cameras
If the NVR is the brain, the PoE cameras are the eyes. These are your vigilant sentinels on the front lines, capturing everything that happens in their line of sight. The real beauty of PoE is that a single Ethernet cable provides both power and data, so you can mount them exactly where you need them—under an eave, on a garage, or overlooking a side yard—without ever needing to find a nearby electrical outlet.
The quality of your video footage is only as good as the cameras capturing it. Here are the key specs to pay attention to:
- Resolution: This is all about clarity. You'll see it measured in megapixels (MP) or terms like 1080p, 2K, and 4K. Higher resolution gives you a sharper image, which is crucial for making out details like faces or license plates from a distance.
- Night Vision: Most cameras use infrared (IR) LEDs to see in total darkness, which gives you a clear black-and-white picture. Some of the newer, more advanced models even offer color night vision, which can be a game-changer for identifying details at night.
- Field of View: This simply tells you how wide of an area the camera can see. A wide field of view is perfect for covering a large open space like a backyard. A narrower view is better for zeroing in on a specific point of entry, like a front door or gate.
The PoE Switch or Injector
The PoE switch is the unsung hero of the system. It’s the central hub for both power and data distribution. Picture it as a smart, heavy-duty power strip designed specifically for your network devices. You plug all your cameras into its ports, and it automatically sends the right amount of electricity to each one while also managing all the video data flowing back to your NVR.
For a really small setup with just one or two cameras, you might opt for a PoE injector instead. It's a simple, compact adapter that "injects" power into a single Ethernet cable that runs between your camera and the NVR.
Your system’s reliability hinges on a clean, stable power supply. A good PoE switch ensures every camera gets consistent power, which prevents frustrating issues like random reboots or dropped video feeds right when you need them most.
Ethernet Cabling: The Lifeline
Finally, we have the Ethernet cables. These are the physical lifelines that tie your entire system together, carrying both the low-voltage power and the high-resolution video data. For any modern PoE camera system, you'll be using either Cat5e or Cat6 cables.
While Cat5e works fine, I almost always recommend going with Cat6. It provides better performance, is less susceptible to interference, and is more future-proof, easily handling the demands of 4K cameras and beyond. Just remember that the maximum length for a single cable run is 100 meters (328 feet), which is plenty of runway for even very large homes.
How to Choose the Right PoE Power Standard
Not all Power over Ethernet is created equal, and this is one of those details that can make or break your security camera system. Think of it like trying to power a high-performance gaming laptop with a tiny phone charger—it just won't work. The same idea applies here.
Every camera has a specific power appetite, and your PoE switch or injector has to serve up enough juice to satisfy it. If you don't, you'll run into frustrating problems like random reboots, lost connections, or features like night vision IR lights failing to turn on. Getting the power match right is absolutely essential for a stable system.
Decoding the IEEE 802.3 Standards
The official names for these power levels come from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), but don't let the alphabet soup intimidate you. These standards—like 802.3af, 802.3at, and 802.3bt—are just different generations of the same technology, each one more powerful than the last. For a home setup, you really only need to know these three.
The beauty of these standards is that they guarantee compatibility. Any camera that follows the standard will work with any switch that does, so you can mix and match brands without worrying.
Here’s the breakdown:
- 802.3af (PoE): This is the original, offering up to 15.4 watts of power. It’s plenty for your basic, no-frills devices like a simple fixed IP camera, a VoIP desk phone, or a standard wireless access point.
- 802.3at (PoE+): The next generation, PoE+, nearly doubles the power to 30 watts per port. This is the sweet spot for more capable security cameras, especially Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) models that have hungry motors to power.
- 802.3bt (PoE++): Sometimes called Ultra PoE, this standard is the heavy hitter, delivering from 60 to 100 watts. It’s built for power-draining equipment like complex video conferencing systems or multi-sensor cameras—definitely overkill for most home security projects.
Key Takeaway: Always check the power consumption (in watts) on your camera's spec sheet. Then, make sure your PoE switch or injector explicitly supports the right standard (PoE, PoE+, or PoE++).
Matching Cameras to the Right Power Source
Let's put this into a real-world context. A simple dome camera watching your porch might only need 5 watts to run, which means a standard 802.3af PoE port is perfect.
But what about a sophisticated PTZ camera meant to scan your entire backyard? Its motors, powerful zoom lens, and advanced sensors need a lot more power. That kind of camera demands an 802.3at (PoE+) port to operate reliably.
Plugging a PoE+ camera into a standard PoE port is a classic rookie mistake. It might light up initially, but the second you try to pan, tilt, or zoom, it will likely shut down. This is exactly why checking the specs before you buy is so critical. To get the best performance, you also need the right wiring; understanding the nuances between Cat 6 vs Cat 7 cabling is a great place to start.
To make things even clearer, here’s a quick reference table that breaks down the standards.
Comparing PoE Power Standards
This table simplifies the technical jargon, helping you quickly match your cameras and other devices to the correct PoE power level.
| PoE Standard | Also Known As | Max Power Per Port | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| 802.3af | PoE | 15.4W | Basic fixed IP cameras, VoIP phones |
| 802.3at | PoE+ | 30W | PTZ cameras, multi-radio access points |
| 802.3bt | PoE++ | 60W – 100W | High-power devices, building management systems |
Keep this handy when you're shopping for equipment. A quick glance can save you from the headache of buying incompatible gear and ensure your system runs smoothly from day one.
Planning Your Home Camera Layout and Installation
A great PoE security camera system doesn't start with drilling holes. It starts with a solid plan. Seriously, mapping out where your cameras will go and how the cables will get there is the single most important thing you can do to avoid headaches later. A little bit of strategy up front ensures you get maximum coverage where it counts, building a security net without any glaring blind spots.
Before you even think about picking up a drill, grab a notepad and walk your property. Put yourself in the shoes of a potential intruder. Where are the weak spots? The goal here is to find the most critical spots to monitor—the places that give you the most bang for your buck, security-wise.
Identify Your Critical Monitoring Zones
First things first, you need to pinpoint the absolute must-have locations for your cameras. I find it really helps to sketch a quick floor plan of your property.
Here are the usual suspects:
- Entry and Exit Points: Every single door is a priority. Front door, back door, patio doors, you name it. Don't forget any low, easily accessible windows.
- Driveways and Garages: A camera watching the driveway sees every person and vehicle that approaches. Covering the garage door itself is just as crucial.
- Key Outdoor Areas: Walk the perimeter. Think about side yards, gates, or those little nooks around the corner of the house where someone could lurk unseen.
- Vulnerable Outbuildings: Is there a shed or a detached garage full of tools? Those are prime targets and definitely need a camera.
Once you’ve got your list, you can figure out the best way to run the Ethernet cables. Planning these paths is the key to a clean, professional-looking installation. For some great tips on this, check out our guide on how to properly wire a smart home.
Plan Your Cable Routes and Power Budget
With your camera spots picked out, it's time to talk logistics. The magic of PoE is that you only need one cable for both power and data, but that cable has to go somewhere. The cleanest installs often involve running cables through an attic, basement, or crawlspace. Just keep the golden rule in mind: a single Ethernet run can't exceed 100 meters (or 328 feet), or you'll risk losing the signal.
Equally important is figuring out your power budget. This is simply the total amount of power your PoE switch can supply to all cameras at the same time.
To calculate this, just add up the maximum power consumption (look for the wattage on each camera's spec sheet) for every camera you plan to connect. Your PoE switch's total power budget must be higher than that sum. This ensures every camera gets the steady power it needs to run reliably.
This little diagram is a great way to see how PoE standards have grown to accommodate more power-hungry devices over the years.
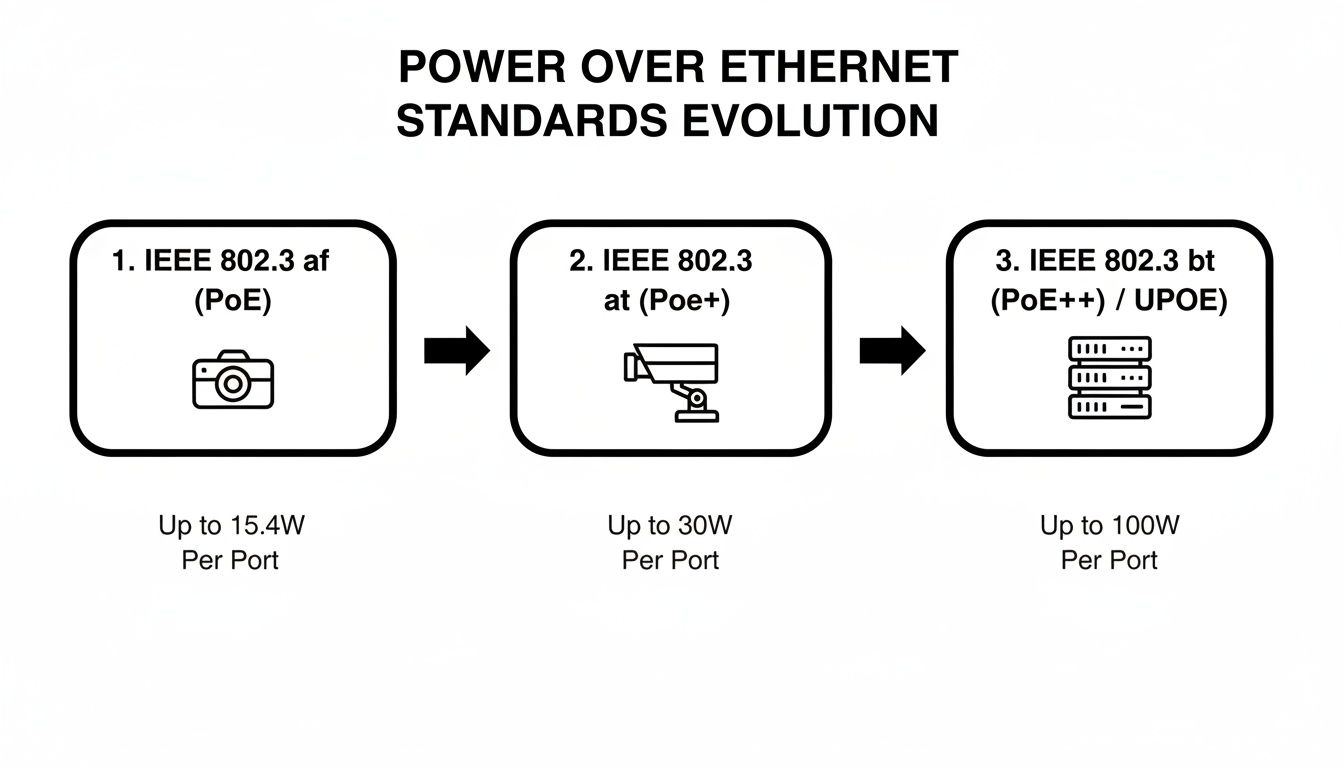
As you can see, moving from the original PoE standard up to PoE++ gives you a massive boost in power, which is essential for running more advanced cameras with features like powerful infrared lights or built-in heaters.
Finding the Perfect PoE Security Camera System for You
Let's be honest, diving into the world of PoE security camera systems can feel like you need an engineering degree. Between all the technical jargon and the sheer number of options, it's easy to get overwhelmed. But here's the secret: you don't need to know everything.
The key is to cut through the noise and focus on what actually matters for your home. By thinking through a few core areas—video quality, how much storage you’ll need, and which smart features are genuinely useful—you can build a system that gives you real peace of mind without paying for extras you'll never use.
Decoding Video Resolution: 2K vs 4K
One of the first things you'll see advertised is video resolution, usually a choice between 2K (4MP) and 4K (8MP). Both are a huge step up from old 1080p cameras, but the difference between them is bigger than you might think.
Imagine 2K is like a good, clear photo on your phone. You can easily see what’s going on and recognize faces. Now, think of 4K as a professional, high-resolution print. The image is so sharp you can zoom way in on something in the background and still see the fine details.
For home security, that extra detail is everything:
- Identifying Faces: A 4K camera is much better at capturing a crystal-clear image of a person's face, especially from a distance.
- Reading License Plates: Trying to make out the license plate on a suspicious car down the street? 4K gives you a fighting chance. 2K often turns into a blurry mess when you zoom in that far.
- Overall Clarity: With 4K, there’s just less guesswork. You get a crisper, more definitive view of your property.
While 2K is perfectly fine for general monitoring, 4K is the clear winner if you need footage that could serve as actual evidence. That extra detail can make all the difference.
Calculating Your NVR Storage Needs
Your Network Video Recorder (NVR) is the brain of the operation, storing all your video footage on its internal hard drive. The last thing you want is to need a recording from last week, only to find it's already been overwritten. That’s why figuring out your storage needs upfront is so critical.
A few things determine how fast you'll fill up that hard drive:
- Number of Cameras: Pretty simple—more cameras mean more video streams, which eats up space faster.
- Video Resolution: A 4K camera will use about twice as much storage space as a 2K camera.
- Recording Mode: Are you recording 24/7 or only when motion is detected? Non-stop recording will chew through storage much, much faster.
- Video Compression: Look for modern systems that use H.265 compression. It’s a smart technology that shrinks video file sizes way down without a noticeable drop in quality.
Rule of Thumb: For a typical four-camera 4K system set to record only on motion, a 2TB hard drive should easily hold several weeks of footage. If you're planning to record 24/7 with that same setup, I’d recommend starting with at least 4TB.
Many NVRs let you add more storage down the road, but it's always a good idea to start with more than you think you need. For a deeper dive into how different camera technologies affect storage and other factors, check out our guide on the differences between IP and analog cameras.
Essential Smart Features vs. Nice-to-Haves
Modern PoE systems are packed with AI-powered features. Some are absolute game-changers for security, while others are more like cool party tricks. Knowing which is which will help you put your money where it counts.
Must-Have Smart Features:
- Person and Vehicle Detection: This is, without a doubt, the most important smart feature. It lets your cameras tell the difference between a person walking up your driveway and a tree branch swaying in the wind. This drastically cuts down on the flood of false alarms that plague older systems.
- Color Night Vision: Traditional infrared night vision gives you a grainy, black-and-white image. Color night vision uses even faint ambient light (from a streetlamp, for example) to produce a full-color video. This makes it infinitely easier to identify the color of a car or a person's clothing after dark.
Features That Are Nice to Have:
- Two-Way Audio: The ability to speak through your camera's speaker is great for telling a delivery driver where to leave a package or startling a would-be trespasser.
- Smart Home Integration: Top-tier systems from brands like Lorex often connect with assistants like Alexa for voice commands. It's a neat convenience. Features like efficient H.265 compression, wide 180° fields of view, and color night vision are also quickly becoming standard.
- Active Deterrence: Some cameras come with a built-in siren or a bright spotlight that can be triggered by motion to actively scare off intruders.
Since over 73.3% of surveillance is for outdoor monitoring, you'll find that manufacturers are heavily focused on building tough, weatherproof cameras. You can see more data on this in the growing surveillance camera market report at Mordor Intelligence.
By prioritizing high-resolution video, plenty of storage, and smart alerts that actually matter, you'll be well on your way to building a powerful PoE system that gives you reliable, meaningful protection.
Troubleshooting Common PoE Installation Issues
Even with the best-laid plans, a DIY installation can hit a snag. It’s incredibly frustrating when a camera you just mounted refuses to power on or when you can't get a video feed to show up. But before you start thinking you got a lemon, take a breath. The fix is usually surprisingly simple.
Most of the time, the problem isn't the camera or the NVR itself. It's almost always something in the connection between them. A methodical approach to troubleshooting, starting with the most obvious stuff first, will solve the vast majority of issues and get your PoE security camera system up and running.
Start with Physical Connections
Your first move should always be a hands-on check of the hardware. It's a basic list, but you’d be surprised how often it solves the problem right away.
- Check Both Ends of the Cable: Is the Ethernet cable clicked in securely? I mean really clicked in. A slightly loose connection at the camera or the NVR is the number one cause of power and data dropouts.
- Test the Cable: If the connection feels solid but the camera’s still dead, the cable itself might be faulty. Grab a spare Ethernet cable that you know works and test the camera with it. If it powers up, you’ve found the culprit.
- Verify the Port: Try plugging the camera into a different PoE port on your NVR or switch. It's rare, but ports can fail. This quick swap will tell you if the port is the problem.
Pro Tip: When a camera won’t power on, it’s almost always a power delivery issue. Before you even think about the camera being defective, focus all your attention on the cable, the port, and your PoE switch’s power budget.
Addressing Power and Network Issues
If all the physical connections are good to go, it's time to look at the power and network side of things. These issues can feel a bit more technical, but they're still pretty straightforward to figure out.
One of the most common mistakes is accidentally exceeding the power budget of your PoE switch. Think of it like a power strip—it only has so much juice to give. If you have five cameras that each need 10 watts, but your switch can only deliver a total of 40 watts, that fifth camera you plug in is getting nothing. Check the specs for your cameras and your switch to make sure you have enough power to go around.
You might also be dealing with a simple network hiccup.
- Confirm Network Settings: Make sure your NVR and cameras are playing on the same team—meaning, they're on the same network subnet. Most plug-and-play kits handle this automatically, but a wrong setting will make your cameras invisible to the NVR.
- Check for IP Conflicts: In some rare cases, two devices on your network might accidentally get assigned the same IP address, causing a conflict that kicks one of them offline. A simple reboot of your router and NVR usually fixes this by letting them hand out fresh addresses.
Fixing Video Quality Problems
What if the camera is online but the picture looks terrible, especially at night? This is usually an issue with the camera's placement or a simple setting.
For example, blurry or washed-out night vision is a classic sign of IR glare. This happens when the camera's built-in infrared lights bounce off a nearby surface—like the soffit of your roof or a close wall—and blast right back into the lens. Simply moving the camera a few inches or changing its angle can make a world of difference.
Frequently Asked Questions About PoE Camera Systems
Diving into a new project like a PoE camera system always brings up a few last-minute questions. It's totally normal. Let's walk through some of the most common things people ask, so you can feel confident you're making the right calls for your home.
Can I Just Use Any Ethernet Cable I Have Lying Around?
Not all Ethernet cables are created equal, and for a PoE system, this really matters. While an old cable might technically connect, it's not a great idea for the long haul.
You'll want to use Cat5e as your absolute minimum, but I strongly recommend going with Cat6 from the start. Cat6 cable is built better to handle interference and provides a much more stable pipeline for both power and the data-heavy video from today's high-resolution cameras. Skimping here can lead to frustrating performance drops and connection issues later on.
How Much Power Do These Cameras Actually Use?
You'll be pleasantly surprised at how little electricity PoE cameras sip. It's one of their biggest perks.
- A standard fixed camera, like a bullet or dome model, typically uses only 4 to 8 watts.
- Even a more complex Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) camera, with motors and powerful night vision LEDs, usually stays in the 15 to 25-watt range.
Honestly, running everything back to a single PoE switch is almost always more energy-efficient than plugging in a separate power adapter for every single camera.
Expert Tip: The smoothest path is to buy a complete, matched system from one manufacturer. This ensures that all the cool features you paid for, like smart person detection or specific video analytics, work together flawlessly right out of the box.
Is It Okay to Mix and Match Camera and NVR Brands?
While you technically can sometimes get different brands to talk to each other using a standard called ONVIF, I really advise against it, especially for a home setup.
Why? Because the most advanced and reliable features are almost always proprietary. If you mix brands, you risk losing access to crucial functions, creating compatibility nightmares, and spending your weekend troubleshooting instead of enjoying your new security system. For a hassle-free experience, stick with a single brand for your NVR and cameras.
Do I Need the Internet for My PoE System to Work?
Nope! A PoE system can run completely offline. It's a self-contained, closed-circuit system where your cameras record directly to the NVR's hard drive without ever needing to touch the internet.
However, you will need an internet connection to use any remote features. If you want to check your live camera feeds from your phone, get motion alerts while you're away, or back up footage to the cloud, you'll need to connect the NVR to your home network. To do that safely, it's a good idea to brush up on some home network security best practices.












Leave a Reply